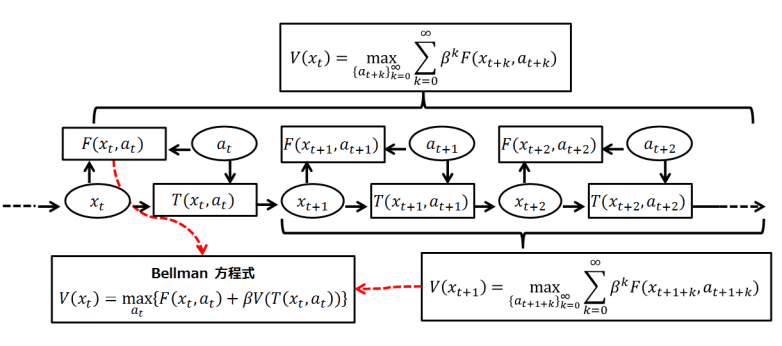
A Bellman equation, named after Richard E. Bellman, is a necessary condition for optimality associated with the mathematical optimization method known as dynamic programming.[1] It writes the “value” of a decision problem at a certain point in time in terms of the payoff from some initial choices and the “value” of the remaining decision problem that results from those initial choices.[citation needed] This breaks a dynamic optimization problem into a sequence of simpler subproblems, as Bellman’s “principle of optimality” prescribes.[2]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bellman_equation
In English understanding,
- Identify the Subproblems/Subphase in Time or Space
- clearly express the recurrence relation with sub problems
- Identify variables of states
- State transition equation (Bellman_equation)
- Define optimisation value Function/Lost function with boundary
In Chinese understanding,
- 识别问题的多阶段性特征
- 将问题分解成递推关系式联系起来的若干个子阶段
- 正确的状态变量
- 正确的定义状态转移方程
- 找到最优的指标函数的递推关系及边界条件
In Programming understanding,
- Define the state(s).
- Define the recurrence relation(s).
- List all the state(s) transitions with their respective conditions.
- Define the base case(s).
- Implement a naive recursive solution.
- Optimize the recursive solution to caching (memoization).
- Remove the overhead of recursion with a bottom-up approach (tabulation).
But the difficulties is in applying in real problem.
Leave a comment